
LoRa Frequencies
What are LoRa freqencies?
LoRa is a spread spectrum modulation technique that operates in the sub-gigahertz frequency bands, specifically the 169 MHz, 433 MHz, 868 MHz, 915 MHz, and 920 MHz bands. It is a proprietary wireless technology developed by Semtech Corporation, and is designed to provide long-range, low-power communication for IoT (Internet of Things) devices.
One of the key features of LoRa is its ability to transmit over long distances, typically up to several kilometers in urban environments and up to tens of kilometers in rural areas. This is achieved through the use of low frequency bands, which have better penetration through buildings and other obstacles, as well as through the use of spread spectrum techniques, which allow the signal to be spread out over a wide frequency range, making it more resistant to interference.
In addition to its long range capabilities, LoRa is also designed to be low power, making it well suited for use in battery-powered IoT devices. It uses a low duty cycle, which means that the radio is only active for a small percentage of the time, and a slow data rate, which reduces the power needed to transmit data.
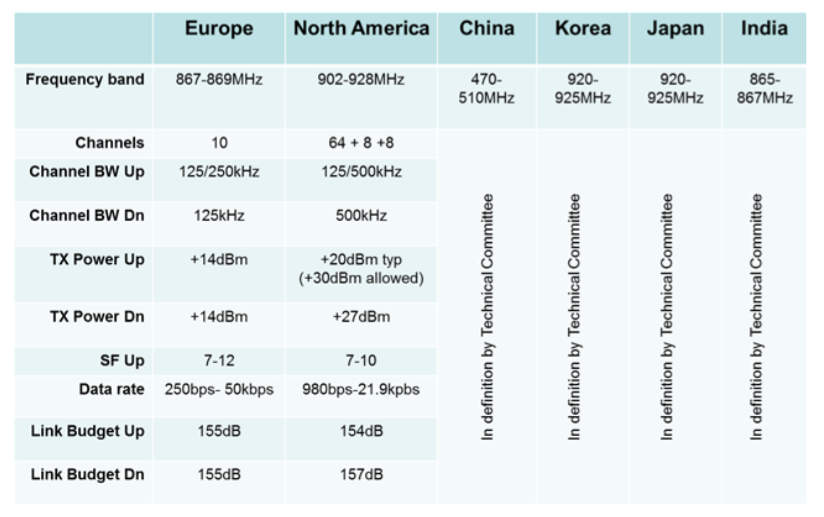
There are several different frequency bands that are used for LoRa communication, depending on the region in which the devices are being used. In Europe, the 868 MHz band is commonly used, while in the United States, the 915 MHz band is more commonly used. There are also other bands that are used in different parts of the world, such as the 169 MHz and 433 MHz bands.
One of the benefits of using the sub-gigahertz frequency bands for LoRa communication is that these bands are typically less congested than the higher frequency bands that are used for other wireless technologies, such as Wi-Fi and cellular. This means that there is less interference and a higher probability of successful communication.
In summary, LoRa is a wireless communication technology that operates in the sub-gigahertz frequency bands and is designed for long-range, low-power communication for IoT devices. It is well suited for use in a variety of applications, including asset tracking, smart metering, and environmental monitoring, due to its long range and low power capabilities.
What are LoRaWAN frequencies?
LoRaWAN is a media access control (MAC) layer protocol that is built on top of the LoRa physical layer, and is designed for use in large-scale public networks. It is a low-power, wide-area networking (LPWAN) protocol that is specifically designed for IoT applications, and is intended to provide a scalable and secure method for connecting a large number of devices to a network over long distances.
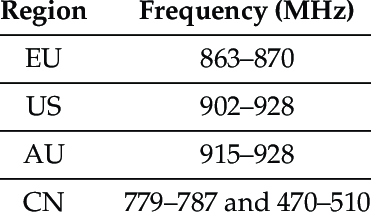
Like LoRa, LoRaWAN operates in the sub-gigahertz frequency bands, including the 169 MHz, 433 MHz, 868 MHz, 915 MHz, and 920 MHz bands. The specific frequency band that is used depends on the region in which the devices are being used. In Europe, the 868 MHz band is commonly used, while in the United States, the 915 MHz band is more commonly used.
One of the key features of LoRaWAN is its use of a decentralized network architecture, in which the communication between devices is facilitated by a network of gateways rather than a central network server. This allows for a highly scalable network that can support a large number of devices.
In addition to its decentralized architecture, LoRaWAN also includes security measures to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of the data being transmitted. These measures include the use of AES-128 encryption for data transmission, as well as the use of unique device keys and network keys to authenticate devices and prevent unauthorized access to the network.
In summary, LoRaWAN is a media access control layer protocol that is built on top of the LoRa physical layer and is designed for use in large-scale public networks. It operates in the sub-gigahertz frequency bands and uses a decentralized network architecture and security measures to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data transmission.



