
What is IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of interconnected physical devices, vehicles, buildings, and other objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and network connectivity. These connected devices collect, exchange, and analyze data, enabling them to communicate with one another and with humans, automating processes and improving efficiency.
IoT has the potential to revolutionize various industries, including agriculture, healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing. Here are some key aspects of IoT:
Sensors and actuators
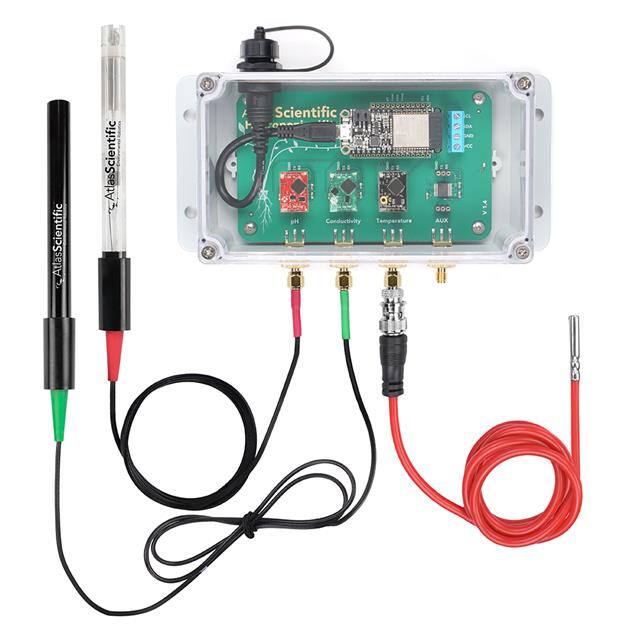

IoT devices are equipped with sensors and actuators that collect data from the environment, such as temperature, humidity, light, motion, or pressure. These devices can also perform actions, such as turning on/off lights, adjusting thermostats, or locking doors.
Connectivity
Devices in IoT networks communicate using various wireless protocols, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Z-Wave, and cellular networks. This connectivity enables real-time data sharing and remote control of devices.
Data processing and analytics
IoT systems often rely on cloud-based platforms or edge computing to process and analyze the vast amounts of data generated by connected devices. This data analysis allows for better decision-making, predictive maintenance, and optimization of processes.
IoT applications
IoT applications encompass a wide range of industries and use cases, leveraging the interconnectedness of devices and systems to improve efficiency, safety, and convenience. Here are some popular IoT applications:
- Smart Homes: IoT devices like smart thermostats, lighting systems, and security cameras enable homeowners to remotely monitor and control various aspects of their homes, optimizing energy usage and enhancing security.
- Wearables: IoT-enabled wearable devices, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, monitor health-related data, like heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity, providing insights to improve well-being.
- Smart Cities: IoT technologies help city planners monitor and manage urban infrastructure, including traffic control systems, waste management, air quality monitoring, and public safety, leading to more efficient and sustainable cities.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): IoT devices in manufacturing and other industrial sectors allow for real-time monitoring of equipment, predictive maintenance, and process optimization, resulting in improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime.
- Agriculture: IoT technologies help farmers monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health, enabling data-driven decision-making for irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, ultimately increasing crop yields and reducing resource waste.
- Healthcare: IoT-enabled medical devices like remote patient monitoring systems and smart drug delivery devices improve patient care, reduce hospital readmission rates, and support remote health management.
- Transportation: IoT technologies, such as telematics and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, enable real-time monitoring and control of fleet vehicles, improving fuel efficiency, safety, and route optimization.
- Energy Management: IoT devices in energy grids can monitor energy consumption and distribution, facilitating smart grid management, demand response, and the integration of renewable energy sources.
- Retail: IoT technologies like smart shelves, inventory tracking systems, and personalized marketing solutions enhance customer experiences, streamline inventory management, and provide insights for retailers to optimize their operations.
- Environmental Monitoring: IoT devices can track environmental parameters like air and water quality, noise pollution, and radiation levels, providing data for governments and organizations to develop and implement environmental policies and regulations.
Security and privacy

Since IoT devices are connected to the internet, they can be vulnerable to cyberattacks. Ensuring the security and privacy of data collected and transmitted by IoT devices is a critical concern for manufacturers, developers, and users.
Interoperability and standardization
With the growing number of IoT devices and applications, it's essential to establish common standards and protocols to ensure seamless communication between devices and systems.
IoT has numerous applications, such as smart homes, where devices can be controlled remotely and work together to optimize energy usage; smart cities, where IoT can help monitor and manage traffic, waste management, and public safety; and industrial IoT (IIoT), which focuses on improving operational efficiency and safety in manufacturing and other industrial sectors. Overall, IoT has the potential to significantly impact our daily lives by automating processes, enhancing efficiency, and providing valuable insights for better decision-making.



