
How IoT is Transforming the Construction Industry
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the construction industry by enhancing efficiency, safety, and productivity. IoT refers to the network of interconnected devices, sensors, and software that collect, analyze, and share data with minimal human intervention. Here are some of the key ways IoT is used in the construction industry:
Equipment and asset tracking
IoT sensors and GPS trackers are attached to construction equipment, tools, and vehicles to monitor their location, usage, and maintenance needs in real-time. This helps to optimize resource allocation, prevent theft, and reduce downtime due to equipment failure.
Wearable technology

Construction workers are equipped with IoT-enabled wearables such as smart helmets, safety vests, and exoskeletons. These devices monitor vital signs, track workers' location, and detect falls or accidents. They can also provide real-time communication with on-site supervisors and emergency services, improving worker safety and reducing the risk of injuries.
Site monitoring

IoT sensors are deployed throughout construction sites to monitor various environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, noise levels, and air quality. This information helps in identifying potential hazards and optimizing working conditions for enhanced productivity and safety.
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
IoT devices are integrated with BIM software to create a digital representation of a construction project. This enables real-time data sharing and collaboration among stakeholders, resulting in better decision-making, improved project coordination, and reduced errors.
Smart buildings

IoT technology is used in constructing smart buildings that are equipped with intelligent systems for energy management, HVAC, lighting, and security. These systems collect data to optimize building performance, reduce energy consumption, and enhance occupant comfort.
Predictive maintenance
IoT sensors installed on equipment and machinery monitor performance data to identify potential maintenance issues before they become critical. This helps in scheduling proactive maintenance, minimizing downtime, and reducing repair costs.
Remote operation
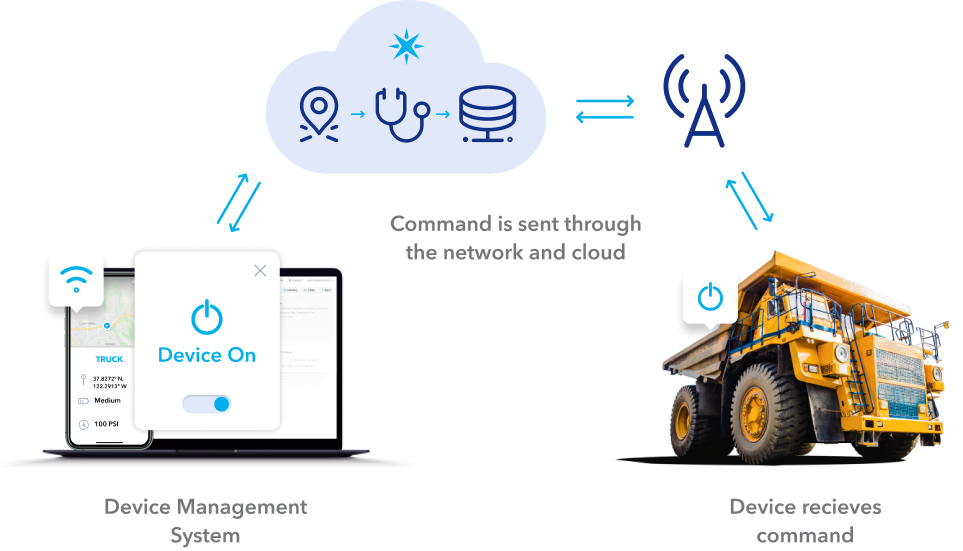
Remote operation in construction refers to the use of technology that allows operators to control equipment and machinery from a distance, without being physically present at the site. This approach is increasingly being adopted in the industry due to its potential to improve safety, efficiency, and productivity. Here are some examples of how remote operation is being used in construction:
- Remote-controlled equipment: Heavy machinery, such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes, can be operated remotely using advanced control systems. Operators can control these machines from a safe location, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries. Remote operation also enables operators to work in hazardous environments, such as those with high levels of noise, dust, or extreme temperatures, without compromising their safety.
- Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or drones: Drones are used to perform various tasks in construction, such as site surveying, progress monitoring, and inspection of hard-to-reach areas. Operators can control drones remotely to capture high-resolution images and videos, which can then be analyzed to make informed decisions related to project planning, scheduling, and resource allocation.
- Robotic systems: Robotic systems, such as autonomous bricklaying and concrete-pouring machines, are remotely operated to perform repetitive and labor-intensive tasks. These systems not only reduce the need for manual labor but also enhance precision and productivity.
- Teleoperation: Teleoperation refers to the remote operation of equipment using virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies. Operators wear VR headsets or use AR displays to visualize the construction site and control equipment remotely. This technology allows for real-time interaction between operators and machinery, providing an immersive experience and improving overall operational efficiency.
- Remote monitoring: Remote monitoring involves the use of IoT sensors, cameras, and other devices to collect data from construction sites, which can then be accessed and analyzed remotely by project managers and stakeholders. This enables real-time decision-making and quick response to any issues that may arise during the construction process.
- Remote collaboration: Cloud-based platforms and communication tools are used to facilitate remote collaboration among construction teams, consultants, and clients. This ensures seamless information exchange and decision-making, even when team members are located in different parts of the world.
Material management

IoT (Internet of Things) plays a significant role in enhancing material management in the construction industry. By integrating sensors, RFID tags, GPS trackers, and data analytics, IoT enables better tracking, monitoring, and optimization of material usage and inventory management. Here are some ways IoT is helping with material management in construction:
Real-time inventory tracking
IoT sensors and RFID tags attached to materials and equipment allow for real-time tracking of inventory levels at construction sites and warehouses. This information can be accessed remotely by project managers and procurement teams, enabling them to make informed decisions on when to order materials and avoid delays due to stockouts or excess inventory.
Supply chain visibility
IoT-enabled devices can monitor the movement of materials throughout the supply chain, from suppliers to job sites. This enhanced visibility helps construction companies better manage logistics, streamline deliveries, and reduce lead times, ensuring materials are available when needed.
Waste reduction
IoT sensors can collect data on material usage, enabling project managers to identify areas of waste or inefficiency. This information can be used to implement better material handling practices, optimize resource allocation, and reduce overall material wastage, resulting in cost savings and a reduced environmental impact.
Predictive analytics
IoT devices collect vast amounts of data related to material usage and supply chain performance. By leveraging advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms, construction companies can identify patterns and trends, enabling them to predict future material requirements and make data-driven decisions for procurement and inventory management.
Quality control
IoT sensors and cameras can be used to monitor the quality of materials delivered to construction sites. By detecting damaged or substandard materials early, construction companies can avoid potential rework, delays, and additional costs.
Automated replenishment
IoT-enabled devices can be integrated with inventory management systems to automate the reordering of materials when inventory levels fall below a predefined threshold. This ensures timely replenishment and reduces the risk of project delays due to material shortages.
Environment monitoring
IoT sensors can monitor environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, at construction sites and storage facilities. This helps ensure materials are stored under optimal conditions, preventing damage or degradation and maintaining the quality of materials.
Quality control
IoT sensors and cameras are used to monitor the quality of construction work in real-time. This enables rapid detection and correction of defects or deviations from project specifications, ensuring higher quality standards and reducing rework costs.
Energy efficiency

IoT (Internet of Things) plays a crucial role in smart metering by enabling real-time data collection, analysis, and communication between meters, utilities, and consumers. Smart meters are digital devices that measure and record energy, water, or gas consumption at regular intervals and transmit the data to utilities and users through IoT-enabled networks. Here are some ways IoT is used in smart metering:
Real-time data collection
IoT-enabled smart meters collect and transmit consumption data in real-time or near-real-time. This allows utilities to have a more accurate and timely understanding of energy, water, or gas usage patterns, enabling better demand forecasting and resource allocation.
Remote monitoring and control
IoT technology enables remote monitoring and control of smart meters. Utilities can access consumption data, detect issues, and perform maintenance tasks remotely without having to physically visit the metering site. This saves time, reduces operational costs, and improves overall efficiency.
Demand response management
IoT-enabled smart meters can be integrated with home automation systems and smart appliances to enable demand response programs. These programs help utilities manage peak demand by incentivizing consumers to reduce or shift their energy consumption during peak hours. IoT technology facilitates communication between utilities and smart devices, allowing for real-time adjustments in energy usage based on grid conditions.
Energy conservation
Smart meters provide consumers with detailed information about their energy, water, or gas consumption, helping them understand their usage patterns and identify opportunities for conservation. By analyzing the data provided by IoT-enabled smart meters, users can make informed decisions to optimize their consumption habits and reduce their utility bills.